Inductance is to wind the wire into a coil shape. When the current flows, a strong magnetic field will be formed at both ends of the coil (inductor). Due to the effect of electromagnetic induction, it will hinder the change of current. Therefore, the inductance has a small resistance to DC (similar to short circuit) and a high resistance to AC, and its resistance is related to the frequency of the AC signal. The higher the frequency of AC current passing through the same inductive element, the greater the resistance value.
Inductance is an energy storage element that can convert electric energy into magnetic energy and store it, usually with only one winding. Inductance originated from the iron-core coil used by M. Faraday in England in 1831 to discover the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Inductance also plays an important role in electronic circuits.
Inductance characteristics: DC connection: refers to that in DC circuit, there is no blocking effect on DC, which is equivalent to a straight wire. Resistance to AC: The fluid that blocks AC and produces a certain impedance. The higher the frequency, the greater the impedance generated by the coil.
Current blocking effect of inductance coil: the self-induced electromotive force in the inductance coil is always resistant to the current change in the coil. Inductive coil has a blocking effect on AC current. The blocking effect is called inductive reactance XL, and the unit is ohm. Its relationship with inductance L and AC frequency f is XL=2nfL. Inductors can be mainly divided into high frequency choke coil and low frequency choke coil.

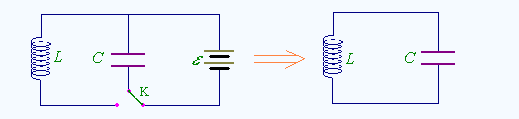
Tuning and frequency selection: LC tuning circuit can be formed by parallel connection of inductance coil and capacitor. That is, if the natural oscillation frequency f0 of the circuit is equal to the frequency f of the non-AC signal, the inductive reactance and capacitive reactance of the circuit are also equal, so the electromagnetic energy oscillates back and forth in the inductance and capacitance, which is the resonance phenomenon of the LC circuit. During resonance, the inductive reactance and capacitive reactance of the circuit are equivalent and reverse. The inductive reactance of the total current of the circuit is the smallest, and the current amount is the largest (referring to the AC signal with f=”f0″). The LC resonant circuit has the function of selecting the frequency, and can select the AC signal with a certain frequency f.
Inductors also have the functions of filtering signals, filtering noise, stabilizing current and suppressing electromagnetic interference.
Post time: Mar-03-2023
